Getting knowledge graph semantics and definitions right. The Year of the Graph Newsletter Vol. 6, October 2018

Getting knowledge graph semantics and definitions right, semantic web standards used in the real world, by Google no less, and ArangoDB, Azure CosmosDB, Neo4j and TigerGraph announcing new versions.
By now you probably know that knowledge graphs are in Gartner’s Hype Cycle. But how does one actually define a knowledge graph? My take on ZDNet.

Knowledge graphs beyond the hype: Getting knowledge in and out of graphs and databases
What exactly are knowledge graphs, and what’s with all the hype about them? Learning to tell apart hype from reality, defining different types of graphs, and picking the right tools and database for your use case is essential if you want to be like the Airbnbs, Amazons, Googles, and LinkedIns of the world.
And here is Stardog’s Kendall Clark’s take:
Alan Morrison from PwC on how Knowledge Graphs can help collapse the IT Stack

Collapsing the IT Stack: Clearing a path for AI adoption
Reduction paradigms can simplify the whole nature of how services are created and delivered. These suggest we could dispense with layers of the stack and enable broad simplification through a model-driven approach. Semantic graph model-driven platforms seem to be on that path.
Did you know Airbnb also has a knowledge graph? You can read about it here. Note the insightful comment on the nuances of building knowledge graphs in the real world from LinkedIn’s manager of taxonomy
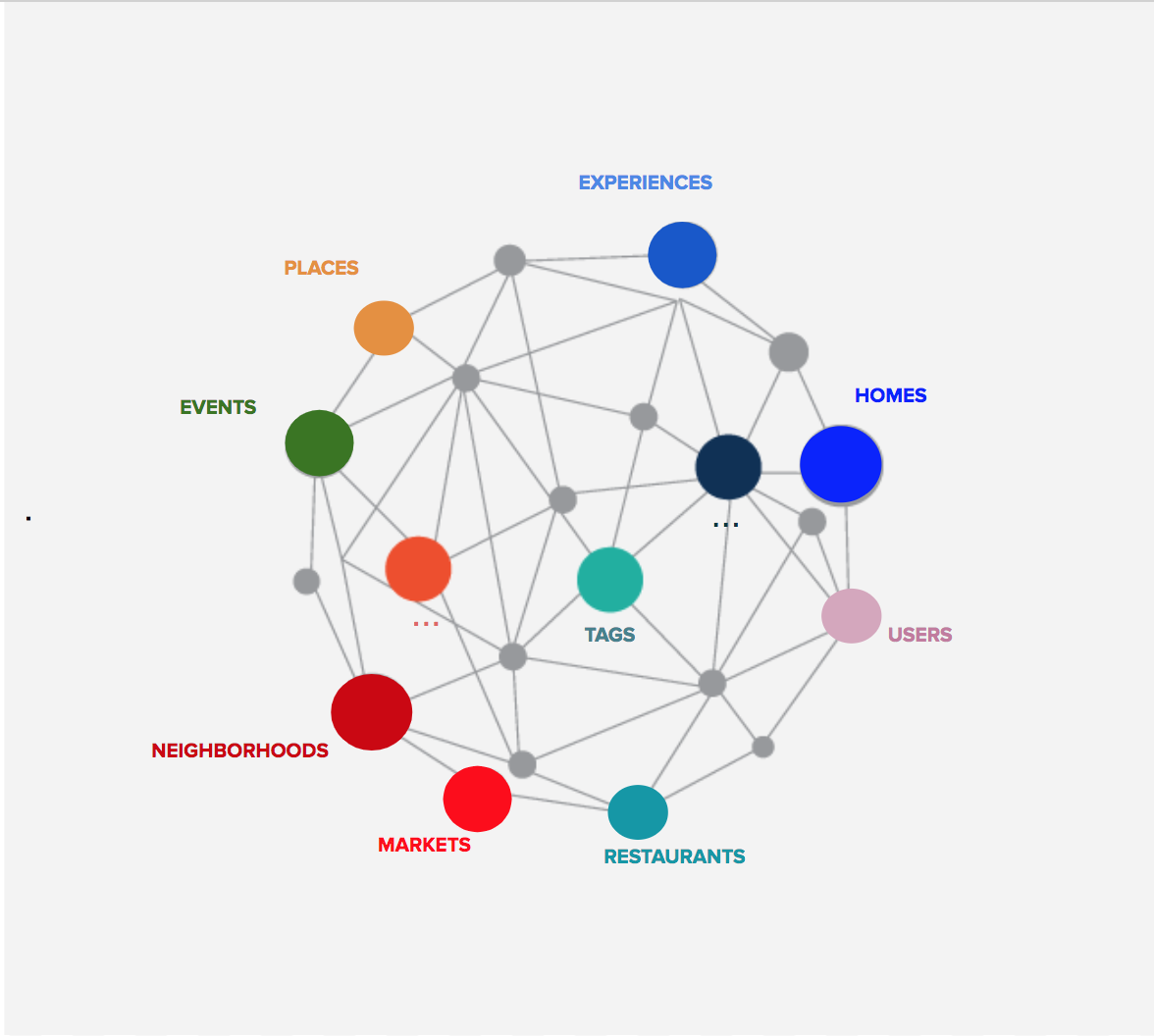
Scaling Knowledge Access and Retrieval at Airbnb
Introducing our Knowledge Graph for encoding relationships and surfacing relevant information
Want to know how knowledge graphs work in the real world? How to handle semantics at web scale, how this helps with data governance, how to evaluate graph databases, or how graphs and AI can work together? Then this is the event for you – check out the program officially announced:

Knowledge Graph and AI Experts for Connected Data London 2018 Program
Connected Data London, the leading event for those who use the relationships, meaning and context in Data to achieve great things, has announced the lineup for the newly expanded Connected Data London 2018, taking place in London on November 7th, 2018.
Cruce Saunders from [A] elaborates on the relevance of the Semantic Web for enterprise publishers

What Is the Semantic Web and Why Should Enterprise Publishers Care?
The Semantic Web is the knowledge graph formed by combining connected, Linked Data with intelligent content to facilitate machine understanding and processing of content, metadata, and other information objects at scale.
Google just expanded search, so now you can also search for data. Besides being very useful, this also shows how schema.org and semantic web standards work in real life:

Google can now search for datasets. First research, then the world?
Did you ever need data on a topic you wanted to research, and had a hard time finding it? Wish you could just Google it? Well, now you can do that.
Dan Brickley, schema.org’s mastermind, on RDF and SPARQL

On using RDF
RDF was designed as a data interchange framework; what you do in the privacy of your own database is your own business
Azure CosmosDB announced new capabilities at Microsoft Ignite 2018. None of those is graph-specific, but things like multi-master at global scale should come in handy regardless

Azure Cosmos DB – database for Intelligent Cloud – Intelligent Edge era
Azure Cosmos DB is Microsoft’s globally distributed, multi-model database service for mission-critical workloads.
Neo4j also announced a new version, 3.5, at Graph Connect NYC. Main new features in v3.5, available in Q4 2018, are full-text search and new graph algorithm implementations.

Neo4j 3.5 Poised to Power the Next Generation of AI & Machine Learning Systems
Latest Neo4j Graph Platform Reveals Context for AI Applications using a Connections-First Approach
A few days before Neo4j, TigerGraph also announced a new version. TigerGraph has added integration with popular databases and data storage systems, announced a github repository to host open source connectors, added support for graph algorithms, and a Neo4j migration kit.

Introducing The Latest Release Of TigerGraph: Fastest Performance For Graph Analytics
Newest Release Features Expanded Toolset, Helping Enterprises Accelerate Time to Value with Graph Analytics
ArangoDB has a new release in the works too: 3.4. A release candidate is available, and main new features are search, support for GeoJSON and Google S2 index, performance improvements via query profiling and streaming cursors, and making RocksDB the default storage engine

RC1 ArangoDB 3.4 – What’s new?
For ArangoDB 3.4 we already added 100,000 lines of code, happily deleted 50,000 lines and changed over 13,000 files until today. We merged countless PRs, invested months of problem solving, hacking, testing, hacking and testing again and are super excited to share the feature complete RC1 of ArangoDB 3.4 with you today.
Wrapping up with some hands-on experience on working with graph databases, shared by Expero’s Josh Perryman

Building Applications on Graph Databases with Josh Perryman
We talk with Josh Perryman of Expero about his experiences building highly scalable and performant applications using relational databases, graph databases and sometimes even both at the same time.